Finite-State Machine as a Type System illustrated with a store product
Hello fellow coders!
In this article, I would like to talk about how to implement a Finite-State Machine (FSM) with the PHP type system. The example is a store product (in an e-commerce solution for instance), something we are likely to meet once in our lifetime. Our goal is to simply avoid impossible states and transitions.
I am in deep love with Type theory, however I will try to keep the formulas away from this article to focus on the code. Moreover, you might be aware that the PHP runtime type system is somewhat very permissive and “poor” (this is not a formal definition), hopefully some tricks can help us to express nice constraints.
The Product FSM
A product in a store might have the following states:
- Active: Can be purchased,
- Inactive: Has been cancelled or discontinued (a discontinued product can no longer be purchased),
- Purchased and renewable,
- Purchased and not renewable,
- Purchased and cancellable.
The transitions between these states can be viewed as a Finite-State Machine (FSM).
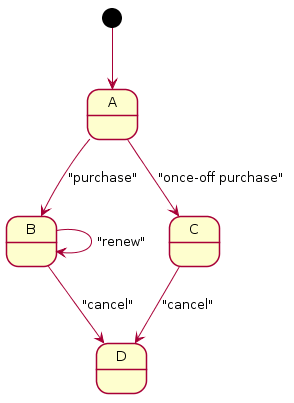
We read this graph as: A product is in the state A. If the purchase
action is called, then it transitions to the state B. If the once-off purchase action is called, then it transitions to the state C. From the
state B, if the renew action is called, it remains in the same state. If
the cancel action is called, it transitions to the D state. Same for the
C to D states.
Our goal is to respect this FSM. Invalid actions must be impossible to do.
Finite-State Machine as a Type System
Having a FSM is a good thing to define the states and the transitions
between them: It is formal and clear. However, it is tested at runtime,
not at compile-time, i.e. if statements are required to test if the
state of a product can transition into another state, or else throw an
exception, and this is decided at runtime. Note that PHP does not really
have a compile-time because it is an online compiler (learn more by
reading Tagua VM, a safe PHP virtual
machine,
at slide 29). Our goal is to prevent illegal/invalid states at
parse-/compile-time so that the PHP virtual machine, IDE or static
analysis tools can prove the state of a product without executing PHP
code.
Why is this important? Imagine that we decide to change a product to be once-off purchasable instead of purchasable, then we can no longer renew it. We replace an interface on this product, and boom, the IDE tells us that the code is broken in x places. It detects impossible scenarios ahead of code execution.
No more talking. Here is the code.
The mighty product
A product is a class implementing the Product interface. It allows to
type a generic product, with no regards about its state.
Active and inactive
The Active and Inactive interfaces are useful to create constraints
such as:
- A product can be purchased only if it is active, and
- A product is inactive if and only if it has been cancelled,
- To finally conclude that an inactive product can no longer be purchased, nor renewed, nor cancelled.
Basically, it defines the axiom (initial state) and the final states of our FSM.
The getProduct(): self trick will make sense later. It helps to
express the following constraint: “A valid product cannot be invalid,
and vice-versa”, i.e. both interfaces cannot be implemented by the same
value.
Purchase, renew, and cancel
Only an active product can be purchased. The action is purchase and it
generates a product that is renewable. purchase transitions from the
state A to B (regarding the graph above).
Only an active product can be cancelled. The action is cancel and it
generates an inactive product, so it transitions from the state B to
D.
A renewable product is also cancellable. The action is renew and this
is a reflexive transition from the state B to B.
Finally, a once-off purchasable product has one action: purchase that
produces a Cancellable product, and it transitions from the state A
to C.
Take a breath
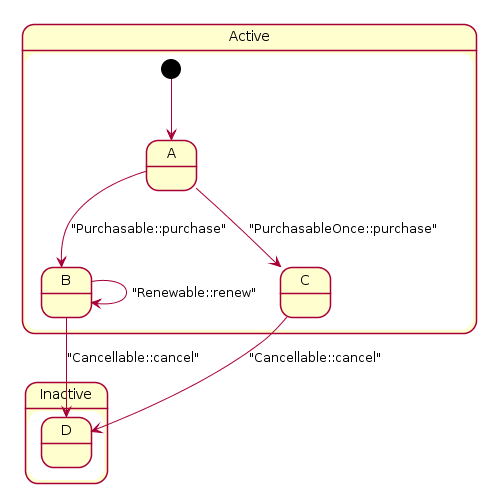
So far we have defined interfaces, but the FSM is not implemented yet. Interfaces only define constraints in our type system. An interface provides a constraint but also defines type capabilities: What operations can be performed on a value implementing a particular interface.
SecretProduct
Let's consider the SecretProduct as a new super secret product that
will revolutionise our store:
The SecretProduct is a product that is active and purchasable. PHP
verifies that the Active::getProduct method is implemented, and that
the Purchasable::purchase method is implemented too.
When this latter is called, it returns an object implementing the
Renewable interface (which is also a cancellable active product). The
object in this context is an instance of an anonymous class implementing
the Renewable interface. So the Active::getProduct,
Renewable::renew, and Cancellable::cancel methods must be
implemented.
Having an anonymous class is not required at all, this is just simpler for the example. A named class may even be better from the testing point of view.
Note that:
- The real purchase action is performed in the constructor of the anonymous class: This is not a hard rule, this is just convenient; it can be done in the method before returning the new instance,
- The real renew action is performed in the
renewmethod before returning$this, - And the real cancel action is performed in… we have to dig a little
bit more (the principle is exactly the same though):
- The
Cancellable::cancelmethod must return an object implementing theInactiveinterface. - It generates an instance of an anonymous class implementing the
Inactiveinterface, and the real cancel action is done in the constructor.
- The
Assert possible and impossible actions
Let's try some valid and invalid actions. Those followings are possible actions:
It is possible to purchase a product, then renew it zero or many times, and finally to cancel it. It matches the FSM!
Those followings are impossible actions:
It is impossible:
- To renew or to cancel a product that has not been purchased,
- To purchase or renew a product that has been cancelled,
- To purchase a product more than once,
- To cancel a product more than once.
Those followings are impossible implementations:
A product cannot be purchasable and once-off purchasable at the same
time, because Purchasable::purchase is not compatible with
PurchasableOnce::purchase.
An inactive product cannot be purchased nor renewed nor cancelled
because Active::getProduct and Inactive::getProduct are not
compatible.
Wow, that's great garantees isn't it? PHP will raise fatal errors for impossible actions or impossible states. No warnings or notices: Fatal errors. Most of them are correctly inferred by IDE, so… follow the red crosses in your IDE.
Restoring a product
One major thing is missing: The state of a product is stored in the database. When loading the product, we must be able to get an instance of a product at its previous state. To avoid repeating code, we will use traits. Rebuilding the state of a product is “just” (it really is) a composition of traits.
Note: In these examples, we are using anonymous classes and traits. It is possible to achieve the same behavior with final named classes. Also we are using a repository, which is convenient for this article, but not necessarily the best solution.
Repository
The following ProductRepository\load function is just here to give you
an idea of how it works.
Traits
The code must look familiar because this is just a split from the
SecretProduct implementation.
Assert possible and impossible actions
The possible actions are:
Product 42 is assumed to be in the state B (Renewable::class), so we
can renew and cancel it.
Those followings are impossible actions:
It is impossible to purchase the product 42 because it is in state B,
so it has already been purchased. It is impossible to cancel a product
twice.
Same garantees apply here!
Conclusion
It is possible to re-implement SecretProduct with the traits we have
defined for the ProductRepository, or to use named classes. I let this
as an easy wrap up exercise for the reader.
The real conclusion is that we have successfully implemented the Finite-State Machine of a product with a Type System. It is impossible to have an invalid implementation that violates the constraints, such as an inactive renewable product. PHP detects it immediately at runtime. Invalid actions are also impossible, such as purchasing a product twice, or renewing a once-off purchased product. It is also detected by PHP.
All violations take the form of PHP fatal errors.
The product repository is an example of how to restore a product at a particular state, with the help of the defined interfaces, and new small and simple traits.
One more thing
It is possible to integrate product categories in this type system (like bundles). It is more complex, but possible.
I would highly recommend these following readings:
- What to know before debating type systems to have an overview of different systems,
- Rust's Type System is Turing-Complete to see how powerful a type system can be,
- Fear Not the Machine of State! to see how to integrate an FSM into an object without using a type system.
I would like to particularly emphasize a paragraph from the first article:
So what is a type? The only true definition is this: a type is a label used by a type system to prove some property of the program's behavior. If the type checker can assign types to the whole program, then it succeeds in its proof; otherwise it fails and points out why it failed.
Seeing types as labels is a very smart way of approaching them.
I would like to thanks Marco Pivetta for the reviews!